
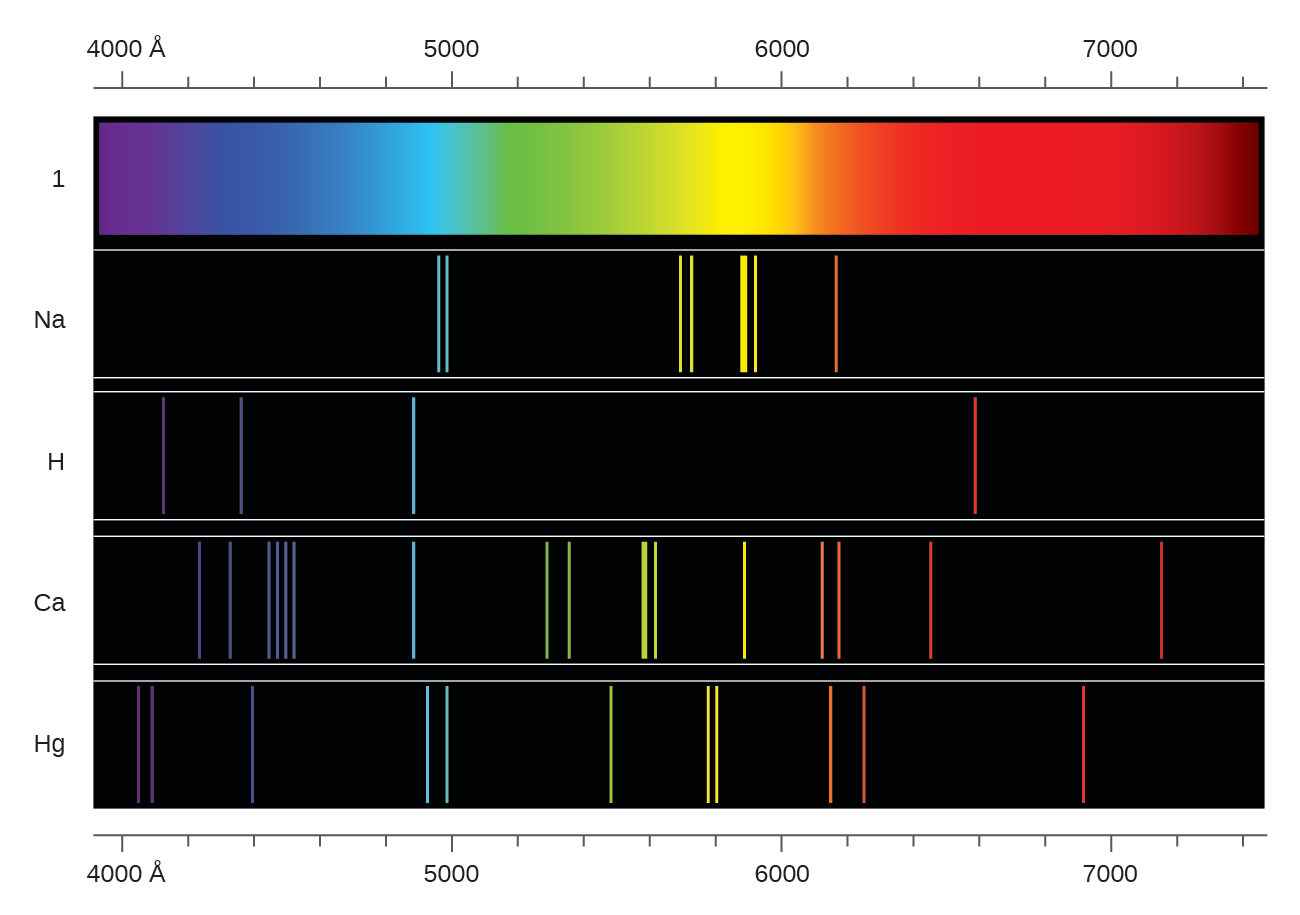
Conversely, as the wavelength decreases, the lines become closer and appear next to one another. If the wavelength of spectral lines is higher and the spacing is greater, the lines appear to be separated, and the wavelength of light can influence these spacings.
Atomic spectra line spectra series#
These spectral series resemble parallel lines of equal length and speed. When the photos are subjected to a spectroscope, each component of this beam of light may generate a different image, which can appear as a spectral series. A beam of light must be directed into the slit to examine these spectrum series. It is the most basic atom with which we may examine the spectral series. The simplest approach to grasp the concept of spectral series is to look at the hydrogen atom. This process generates emission spectra and absorption spectra. This higher energy level is unstable, and hence they need to emit energy within the kind of radiation to return to their original states. The interaction of electromagnetic waves with matter causes the molecules and atoms present in a very large area to absorb energy and reach the next energy level. When the white light is responded to a medium, they get split consistent with their respective frequencies and wavelengths. Microwaves, actinic radiation, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma-rays are kinds of radiation included within the Spectrum. Electromagnetic waves are further classified as portions, and ultraviolet rays and visual light are examples.
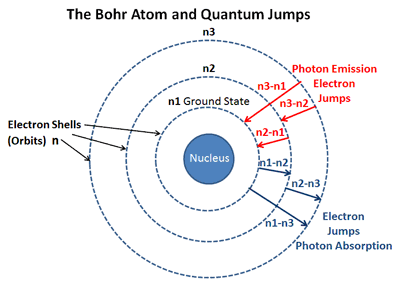
Electromagnetic waves can travel in an exceeding vacuum at the speed of sunshine. A normal light features a large range of wavelengths with respective frequencies.
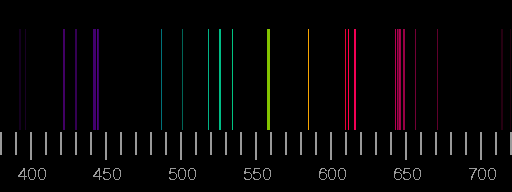
We know that light is radiation composed of several frequencies of radiation. The Pauli exclusion principle asserts that no two half-integer spin particles (such as electrons) in an atom may occupy the same energy state simultaneously thus, the K-shell represents two different energy states, the L-shell eight, and so on. As each element encompasses a specific arrangement of electrons at discrete energy, it is appreciated that the radiation produced from such interactions is ‘characteristic’ of the element involved.Įlectron transitions from the L-shell to the K-shell, for example, yield x-ray photons with energies of 57.98 and 59.32 keV in a tungsten target. The electron within the K-shell is ejected (provided the incident electron’s energy is larger than the separation energy of the K-shell electron), abandoning a ‘hole’ with an emission of one x-ray photon, sometimes called a characteristic photon, with energy equal to the energy state difference between the outer and inner shell electron involved within the transition.Īs critical the continual spectrum of bremsstrahlung radiation, characteristic radiation is represented by a spectrum. This energy emission happens when a fast-moving electron collides with a K-shell electron. Characteristic Spectrum of radiation :Ĭharacteristic radiation may be a style of energy emission relevant for X-ray production.

Emission spectra, absorption spectra, and continuous spectra are the three types of atomic spectra. The atomic spectra of atoms are a collection of all these wavelengths of the atom in a specific range of parameters, such as pressure, temperature, etc. When an electron is excited from one energy level to the next, it emits or absorbs light of a specific wavelength. Each chemical element’s atomic spectrum is distinct, and it is substantially responsible for matter’s colour.ĭuring transitions between different energy levels within an atom, an electron produces or absorbs a spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. The development of quantum mechanics hinged on the explanation of this phenomenon. The energy difference between the orbitals determines the frequency. An electron can hop from one fixed orbital to another: if the orbital it jumps to has higher energy, it must absorb a photon of a particular frequency if the orbital it jumps to has lower energy, it must emit a photon of a specific frequency. An atom has a range of readily absorbed and emitted characteristic frequencies of electromagnetic radiation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
